Interpreter
Interpreter pattern provides a way to evaluate language grammar or expression. This type of pattern comes under behavioral pattern. This pattern involves implementing an expression interface which tells to interpret a particular context. This pattern is used in SQL parsing, symbol processing engine etc
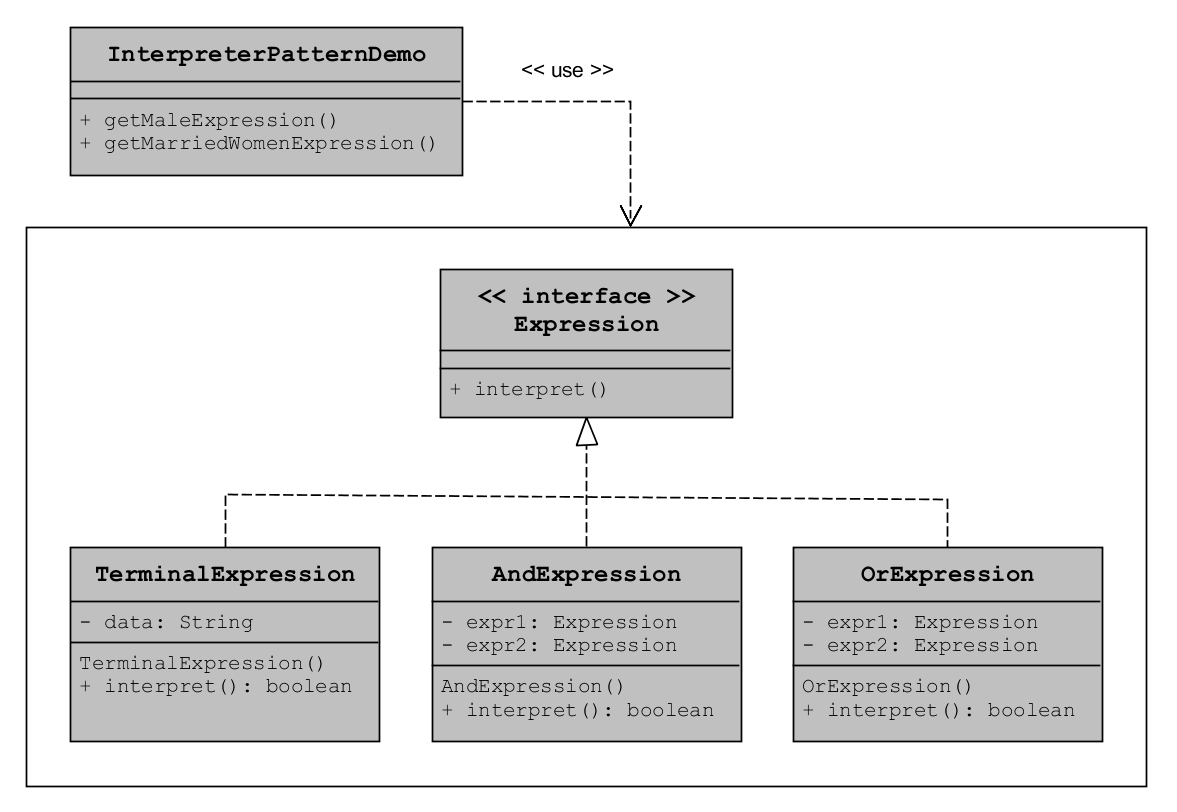
Interpreter in Java recognizable by behavioral methods returning a structurally different instance/type of the given instance/type; note that parsing/formatting is not part of the pattern, determining the pattern and how to apply it is
java.util.Patternjava.text.Normalizer- All subclasses of
java.text.Format - All subclasses of
javax.el.ELResolver
public interface Expression {
public boolean interpret(String context);
}
public class TerminalExpression implements Expression {
private String data;
public TerminalExpression(String data){
this.data = data;
}
@Override
public boolean interpret(String context) {
if(context.contains(data)){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
public class OrExpression implements Expression {
private Expression expr1 = null;
private Expression expr2 = null;
public OrExpression(Expression expr1, Expression expr2) {
this.expr1 = expr1;
this.expr2 = expr2;
}
@Override
public boolean interpret(String context) {
return expr1.interpret(context) || expr2.interpret(context);
}
}
public class AndExpression implements Expression {
private Expression expr1 = null;
private Expression expr2 = null;
public AndExpression(Expression expr1, Expression expr2) {
this.expr1 = expr1;
this.expr2 = expr2;
}
@Override
public boolean interpret(String context) {
return expr1.interpret(context) && expr2.interpret(context);
}
}
public class InterpreterPatternDemo {
//Rule: Robert and John are male
public static Expression getMaleExpression(){
Expression robert = new TerminalExpression("Robert");
Expression john = new TerminalExpression("John");
return new OrExpression(robert, john);
}
//Rule: Julie is a married women
public static Expression getMarriedWomanExpression(){
Expression julie = new TerminalExpression("Julie");
Expression married = new TerminalExpression("Married");
return new AndExpression(julie, married);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Expression isMale = getMaleExpression();
Expression isMarriedWoman = getMarriedWomanExpression();
System.out.println("John is male? " + isMale.interpret("John"));
System.out.println("Julie is a married women? " + isMarriedWoman.interpret("Married Julie"));
}
}